Inductive Effect:
- The polarization of σ bond due to electron withdrawing or electron donating effect of adjacent groups or atoms is called inductive effect.
Salient features of
inductive effect:
- It arises due to electronegativity difference between two atoms forming a sigma bond.
- It is transmitted through the sigma bonds.
- The magnitude of inductive effect decreases while moving away from the groups causing it.
- It is a permanent effect.
- It influences the chemical and physical properties of compounds.
- The inductive effect is divided into two types depending on their strength of electron withdrawing or electron releasing nature with respect to hydrogen.
- The electron withdrawing nature of groups or atoms is called as negative inductive effect. It is indicated by -I. Following are the examples of groups in the decreasing order of their -I effect:NR3+ > NH3+ > NO2 > CN > SO3H > CHO > CO > COOH > COCl > CONH2 > F > Cl > Br > I > OH > OR > NH2 > C6H5 > H
- It refers to the electron releasing nature of the groups or atoms and is denoted by +I. Following are the examples of groups in the decreasing order of their +I effect.C(CH3)3 > CH(CH3)2 > CH2CH3 > CH3 > H
Though the C-H bond is practically
considered as non-polar, there is partial positive charge on hydrogen atom and
partial negative charge on carbon atom. Therefore each hydrogen atom acts as
electron donating group. This cumulative donation turns the alkyl moiety into
an electron donating group.
Electrometric Effect:
- The electrometric effect is the movement of electrons from one atom to another as a reagent attacks a π bond.
- When
the electron transfer takes place towards the attacking reagent, it is called
+E effect.
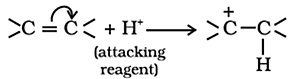
- When
the electron transfer takes place away from the attacking reagent, it is called
- E effect.


No comments:
Post a Comment